Antimetabolites
Mechanism of action:
Inhibit the replication of DNA.
- Cytidine analogs
| Name | Structure |
| Azacytidine | 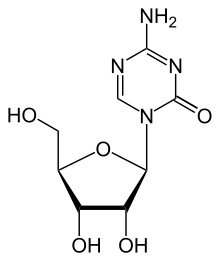 |
| Decitabine | 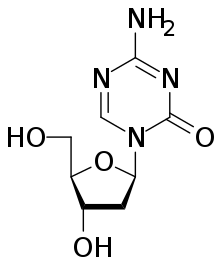 |
| Cytarabine | 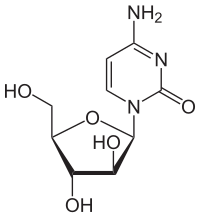 |
| Gemcitabine |  |
MoA: Directly incorporate into DNA and inhibit DNA methyltransferase (azacitidine, decitabine) or DNA polymerase (cytarabine, gemcitabine)
- Indications: Azacitidine and decitabine for MDS, AML, cytarabine for MDS, AML, and gemcitabine for breast, NSCLC, ovarian, pancreatic, bladder, sarcoma, Hodkin lymphoma, NHL
- Toxicity: Myelosuppression in general. Cytarabine high dose causes neurotoxicity, conjunctivitis. Gemcitabine causes liver enzyme elevations, interstitial pneumonitis.
- Folate antagonists
| Name | Structure |
| Methotrexate |  |
| Pemetrexed |  |
MOA: Reduces folate, which is essential in the synthesis of purine nucleotides and thymidylate
- Indications: Methotrexate for ALL, NHL, CNS, sarcoma, and pemetrexed for malignant pleural mesothelioma, NSCLC (non-squamous)
- Toxicity: Myelosuppression, mucositis, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, cutaneous reactions
- Toxicity prevention: Hydration and alkalization of the urine, leucovorin rescue
- Purine analogs
| Name | Structure |
| Cladribine | 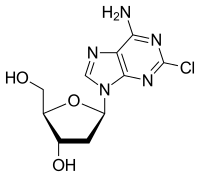 |
| Clofarabine |  |
| Nelarabine |  |
MOA: structural analogs of guanine and act as false metabolites
- Indications: Cladribine for hairy cell leukemia, AML, CLL, NHL. Clofarabine for ALL, AML. fludarabine for CLL, AML, NHL, BMT conditioning agent. Nelarabine for T-ALL, lymphoma. Pentostatin for hairy cell leukemia, CTCL, CLL.
- Toxicities: Myelosuppression, immunosuppression (suppress CD4+ cells) put patients at risk for opportunistic infections
- Pyrimidine analogs
| Name | Structure |
| Fluorouracil (5-FU) |  |
| Capecitabine (prodrug of 5-FU) |  |
MOA: Active metabolite (F-dUMP) forms a stable covalent complex with thymidine synthetase in the presence of reduced folate, therefore, interfering with DNA synthesis and repair.