Epidermal growth factor
- EGF is a message telling cells that they have permission to grow.
- It is released by cells in areas of active growth, then is either picked up by the cell itself or by neighboring cells, stimulating their ability to divide.
- received by a receptor on the cell surface, which binds to EGF and relays the message to signaling proteins inside the cell, ultimately mobilizing the processes needed for growth.
- PDB101
EGFR Inhibitors
A substance that blocks the activity of a protein called epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). EGFR is found on the surface of some normal cells and is involved in cell growth. It may also be found at high levels on some types of cancer cells, which causes these cells to grow and divide. Blocking EGFR may keep cancer cells from growing. Some EGFR inhibitors are used to treat cancer. Also called EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
| Name | Structure |
| Erlotinib | 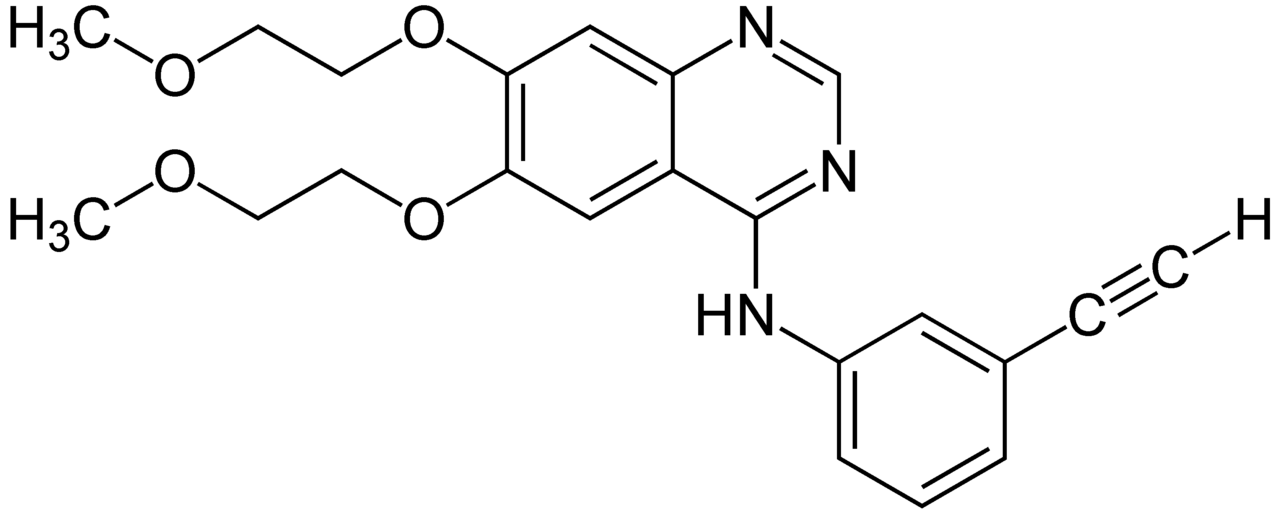 |
| Gefitinib | 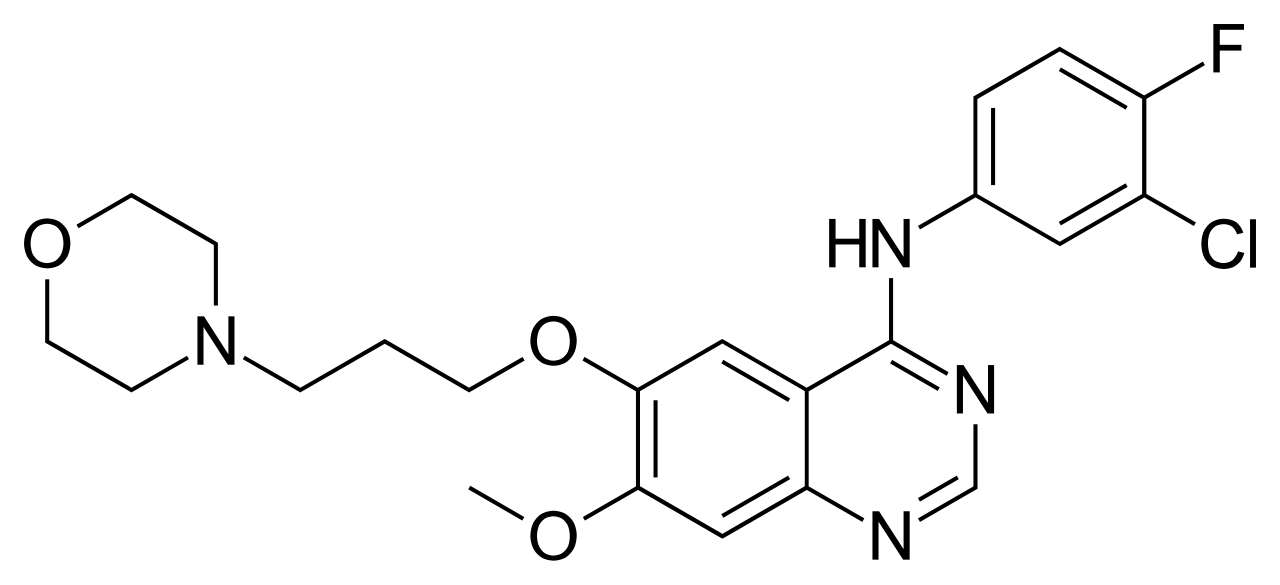 |
| Lapatinib |  |
| Cetuximab | Complex with extracellular domain of EGFR |
| panitumumab | Complex with domain 3 of EGFR |