Cis-platin and analogs
| Name | Structure |
|---|---|
| cis-platin | 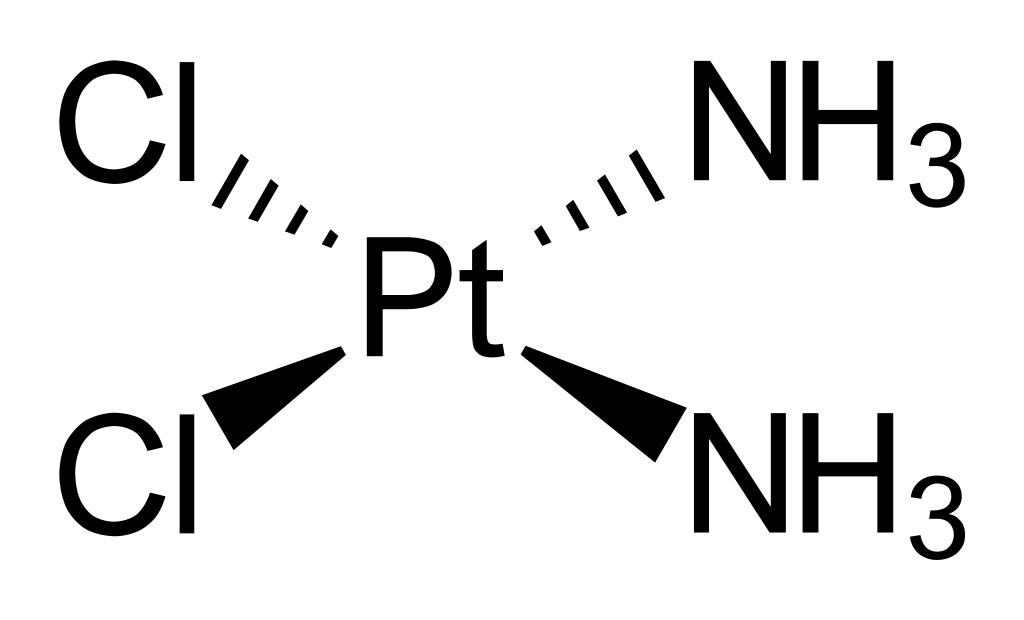 |
| carboplatin | 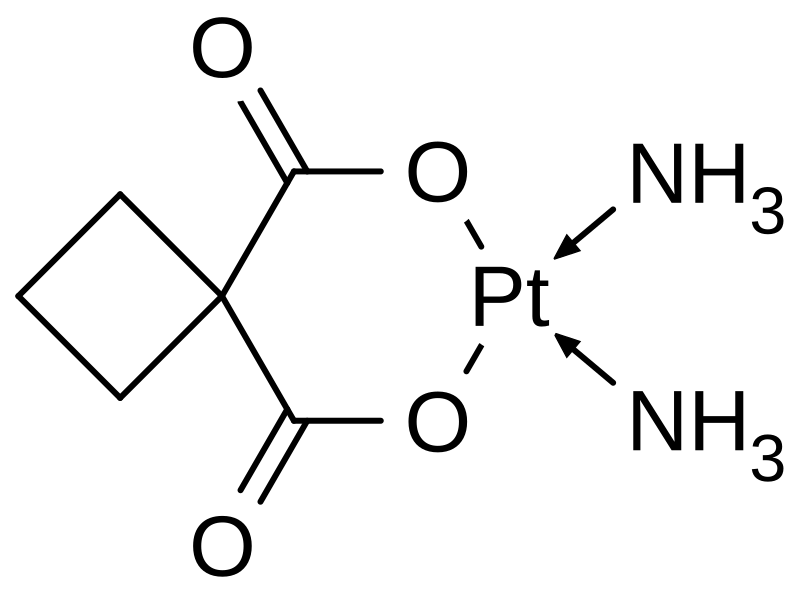 |
| oxaliplatin |  |
Mechanism of action
- Cisplatin crosslinks DNA by binding adjacent guanine bases on a strand.
- Cisplatin affects the cell by changing the conformation of the DNA, and thus, changing how it interacts with proteins.
Interactions with target
Normal DNA: PDB ID 3dnb
Cis-platin bound DNA: PDB ID 3lpv
Proteins of the high mobility group DNA-binding family (HMG-domain proteins) prefer to bind to bent DNA, and thus bind to bent cisplatin-bound DNA, as seen in PDB ID 1ckt. The HMG protein then shields the cisplatin-damaged DNA from other proteins involved in DNA replication, repair, and transcription.
These events collectively trigger apoptosis or programmed cell death.
Resistance
Tumors can develop resistance to cisplatin treatment by several ways, including changing the traffic of cisplatin across the cell membrane and down-regulating mechanisms that cause cell death. Oxaliplatin is used when resistance develops.